10 Best Cybersecurity Practices To Protect Your Business
Cybersecurity has emerged as a need of the hour. The rise of cyberattacks and data theft is on rise. Individuals and businesses mostly rely on computer applications, mobile / IoT devices and cloud storage to handle their data which can be sensitive and personal at the same time. The technological advancements have made conduct of business easier and at the same time the vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks have increased, especially with the increase in use of IoT devices.
Every business, small or big should take necessary cybersecurity measures and implement the most advanced solutions to protect their data to protect themselves from theft of intellectual property, sensitive data and corporate information, which results in huge losses for the business. The impact of cyberattacks can be vast including the cost for repairing the damaged systems.
Cybersecurity solutions combines technologies, processes and methods to protect servers, data and networks from cyber-attacks. Todays cyberattacks can no longer be prevented by firewalls or antivirus software alone. Also, to keep in mind cyber-attacks are inevitable. So how can a business be prepared to face the uncertainties of cyberworld and targeted attacks ensuring the safety of data and networks?
To help with, here is a list of top 10 cybersecurity best practices to help protect your business from cyber-attacks and threats.
1. Keep your employees aware of cybersecurity measures
Employee training is the first and foremost step every management should invest in ensuring cybersecurity. They play a vital role in cybersecurity because they can be the biggest security risk as well as the strongest security defence. Thus, educating them on possible threats, malicious activities and reducing the level of employee negligence is vital. Also never forget to protect access to corporate assets and monitor the employees while handling sensitive data.
2. Update your security policies
Security policies are the backbone of enterprise security. Businesses needs to ensure that they use the latest technologies to address cyber threats and attacks. Implement the latest cybersecurity solutions. There is a number of advanced cybersecurity solutions offered to ensure the high-end data and network security.
Learn more about cybersecurity solutions
3. Enable multi-factor authentication for all users
To keep your accounts safer, always use strong passwords. Hackers often get into the internal sources of a business through compromised user accounts having weak passwords. Thus, to ensure the security of every user’s login, enable two-factor authentication along with a strong password. Multi-factor authentication involves having access cards or pins for critical access / privileged access. This will be an effective measure to prevent cyber-attacks.
4. Install anti-virus and anti-malware software
When you are connected to web, it’s nearly impossible to have a complete control and protection against malwares. The use of anti-virus, anti-malware software and firewalls can help to reduce the vulnerabilities. But for the present world’s scenario, having firewalls and anti-virus software alone is not enough to protect from threats. It requires an extra layer of protection from cyber-attacks such as implementation of advanced threat detection and vulnerability assessment solutions.
Learn more about Network threat detection
5. Protect access to critical data & assets
Access to critical and sensitive data should be monitored efficiently and the management should have control over the privileged accesses to protect theft of key data. To ensure such, access from remote devices should be protected and monitor the user activity through comprehensive technical solution. Its always good to have VPN services for your remote workforce. Also limit the number of users having access to sensitive data.
6. Have a robust cybersecurity policy and network protection plan
Having a clear and concise cybersecurity policy is key to ensure that your business is on the right track to defend cyber-attacks. Implementing too many cybersecurity solutions can also delay the detection of threats in real time. Thus, finding the right solution for your business needs is important. An all-in-one comprehensive solution such as SIEM can be an ideal cybersecurity solution wherein you get a complete cybersecurity picture.
7. Be skeptical while opening emails
There can be a number of spam and suspicious emails that an organisation may receive on a daily basis. The employees should always be conscious while opening an attachment, click on link or provide sensitive information. It may be a hacker impersonating as a company or an individual to get into your internal network. If emails look suspicious it is better to avoid opening them because it can possibly a phishing scam.
8. Avoid using public networks
It is always advised to use private networks rather than connecting to a public network. While connected to a public network, any data shared over the network is vulnerable. Hackers can easily get your data. Private networks on the other hand uses firewalls and internet router to block cyber-attacks.
9. Backup important data
It is important to back up your important data. Data can be lost due to security breach or a targeted cyber-attack. Thus, to ensure that your important data is not permanently gone, always have a backup storage in cloud or local storage devices. An offline backup storage will be a secure option to safeguard your data, always encrypt and backup data regularly.
10. Monitor third party access to your data
Sometimes the third parties such as former employees, consultants or clients may have temporary access to organisation’s network. It is important to keep in mind that, after the particular requirement for which the access was given, it should be restricted.
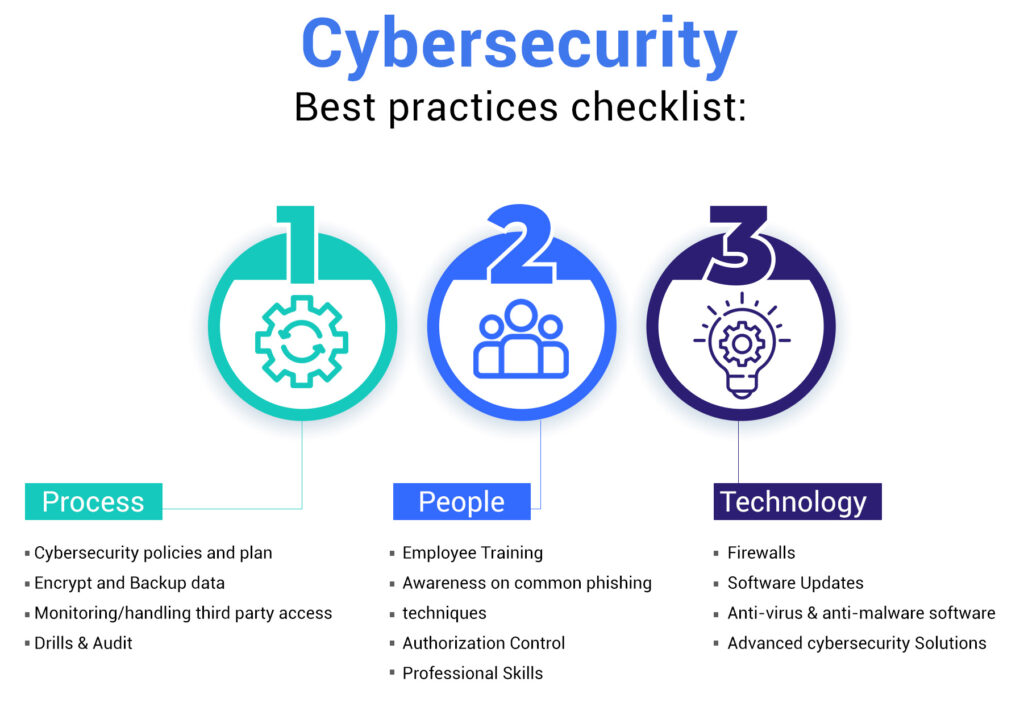
Cybersecurity best practices checklist:
Process
- Cybersecurity policies and plan
- Encrypt and Backup data
- Monitoring/handling third party access
- Drills & Audit
People
- Employee Training
- Awareness on common phishing techniques
- Authorization Control
- Professional Skills
Technology
- Firewalls
- Software Updates
- Anti-virus & anti-malware software
- Advanced cybersecurity Solutions